The search for sustainable and efficient home heating solutions has never been more critical, with rising energy costs and mounting concerns about climate change. One technology at the forefront of this movement is the heat pump. Unlike traditional furnaces or boilers that burn fuel to create warmth, heat pumps transfer heat from the outdoors to indoors, even in chilly climates. Homeowners interested in upgrading their systems increasingly turn to resources like Colorado home heat pump installation to discover high-efficiency solutions tailored to their region and energy needs.
Today’s heat pumps offer a unique combination of efficiency and environmental friendliness, making them a compelling alternative for homeowners focused on cost savings and reducing their carbon footprint. As the push for electrification and clean energy adoption accelerates, heat pumps redefine what’s possible in home heating technology.
What Are Heat Pumps?
A heat pump is a highly efficient device designed to move heat rather than generate it. In heating mode, it draws thermal energy from the air, ground, or even water outside and concentrates it for release inside a home. The refrigeration cycle at the system’s heart is the same technology that keeps your refrigerator cool, reversed for heating. With the change of seasons, modern heat pumps seamlessly switch to cooling mode, efficiently extracting heat from indoors and expelling it outside, serving as an all-in-one climate system for year-round comfort.
This dual functionality is especially advantageous for regions that experience both hot summers and cold winters. Homeowners can benefit from a streamlined installation and maintenance routine, replacing the furnace and air conditioner with one versatile unit.
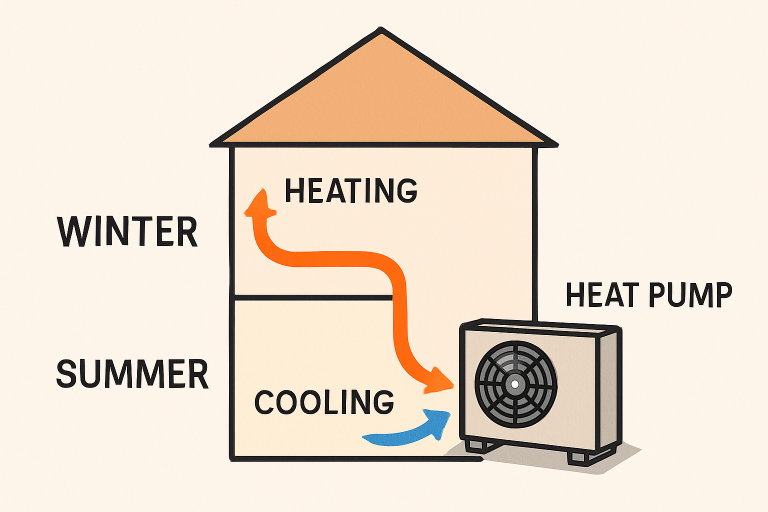
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Heat pumps are distinguished by their impressive energy efficiency ratings. Unlike gas or oil furnaces that use combustion, heat pumps can deliver three to four times more heat energy than the electricity they consume. This is made possible by the physics of heat transfer, which is inherently less wasteful than fuel combustion.
These efficiencies lead to significant cost savings on energy bills, but the benefits don’t stop there. By using less energy, heat pumps dramatically cut household greenhouse gas emissions. According to the International Energy Agency, widespread adoption of heat pumps could slash global CO₂ emissions by around half a gigaton annually, making the transition from fossil fuel heating systems one of the most impactful climate actions homeowners can take.
Technological Advancements
Early generations of heat pumps sometimes struggled in regions with frigid winters, but recent innovations have transformed their capabilities. Cold-climate heat pumps now feature variable-speed compressors, advanced control systems, and superior refrigerants, allowing them to maintain high performance and efficiency even when outdoor temperatures plunge to -22°F (-30°C).
These advancements mean that heat pumps are no longer limited to moderate climates. New technologies have broadened their appeal, making them an option for virtually any home, regardless of location or weather extremes. For homeowners in cold states like Colorado, efficient solutions are now readily available from local experts who are well-versed in regional conditions.
Government Incentives and Policy Support
Recognizing the potential of heat pumps to move the needle on climate action, many governments are offering substantial financial incentives to accelerate adoption. In the U.S., homeowners may be eligible for a 30% tax credit through the Inflation Reduction Act, with the possibility of additional rebates for qualifying income levels. Programs like the United Kingdom’s Boiler Upgrade Scheme further demonstrate international commitment to mainstreaming this technology through grants that offset air and ground source heat pump installations.
These measures make heat pumps increasingly affordable and accessible, equalizing the playing field with traditional equipment and empowering more households to invest in their long-term comfort and sustainability.
Real-World Applications
Heat pumps are proving their versatility in a range of practical installations. In New York City, for instance, the Housing Authority is piloting window-mounted models to deliver efficient heating and cooling in large apartment buildings. This project reduces residents’ utility bills and helps municipal efforts to decarbonize older building stock.
Other communities, such as Framingham, Massachusetts, have taken innovative approaches with ground-source heat pump networks serving entire neighborhoods. Residents and businesses connected to these systems have seen dramatic drops in fuel costs and carbon emissions, underscoring the pivotal role of heat pumps in the broader clean energy transition.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their many benefits, a few hurdles remain in the path to widespread heat pump adoption. The upfront installation cost—especially for systems needing duct upgrades or those replacing aging infrastructure—can be a deterrent for some homeowners. Additionally, home insulation quality, existing ductwork, and climatic extremes influence heat pump effectiveness.
Choosing the right system often means seeking guidance from local professionals who understand the nuances of available technology and regional energy needs. With careful planning and consultation, most homeowners can find a heat pump solution that fits their living space and maximizes comfort, efficiency, and long-term value.
Conclusion
Heat pumps are reshaping the landscape of home heating, offering an eco-friendly, highly efficient alternative that stands at the crossroads of comfort and sustainability. Technological progress and supportive policies ease access and affordability, putting this transformative technology within reach for more homeowners than ever. As adoption grows and success stories multiply across cold and temperate climates alike, heat pumps are poised to play a starring role in the move toward cleaner, more intelligent home energy solutions.


